Have you noticed your Wi-Fi connection slowing down? It’s frustrating, and even the best Wi-Fi routers aren’t immune from occasional connectivity issues. Most of our devices need Wi-Fi to access the Internet, which puts demands on the available bandwidth on our networks. Even if you have fast cable or fiber internet coming into your home, the speeds available on the inside of your walls are down to you. But before you consider upgrading your router, maybe to one of those fancy mesh networks, there are a few things you can try to increase your Wi-Fi speed.

Related
5 reasons why your Wi-Fi might be slow
One wrong setting could kill your Wi-Fi speed
6 Switch the frequency band
And change to an uncongested broadcast channel
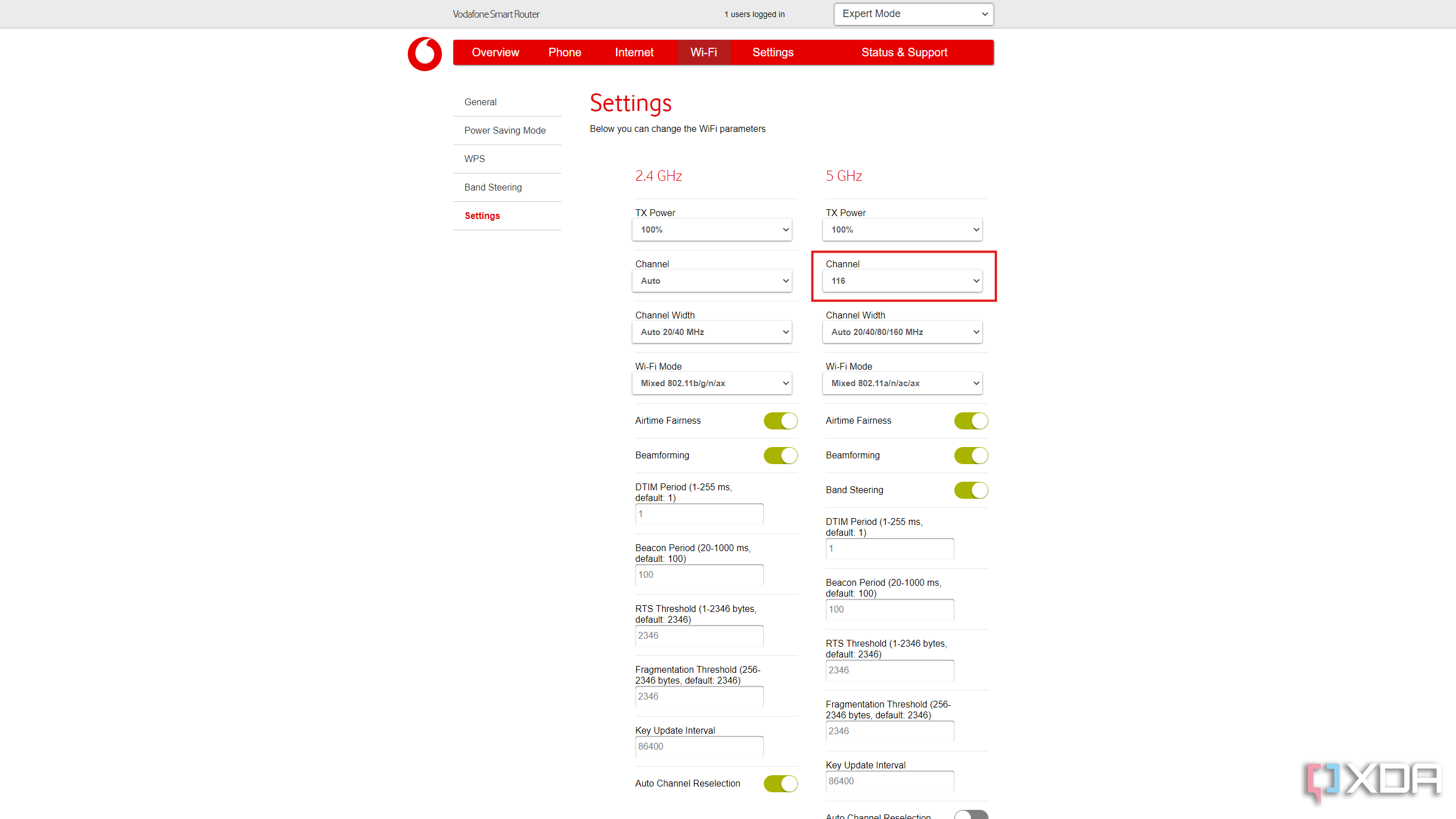
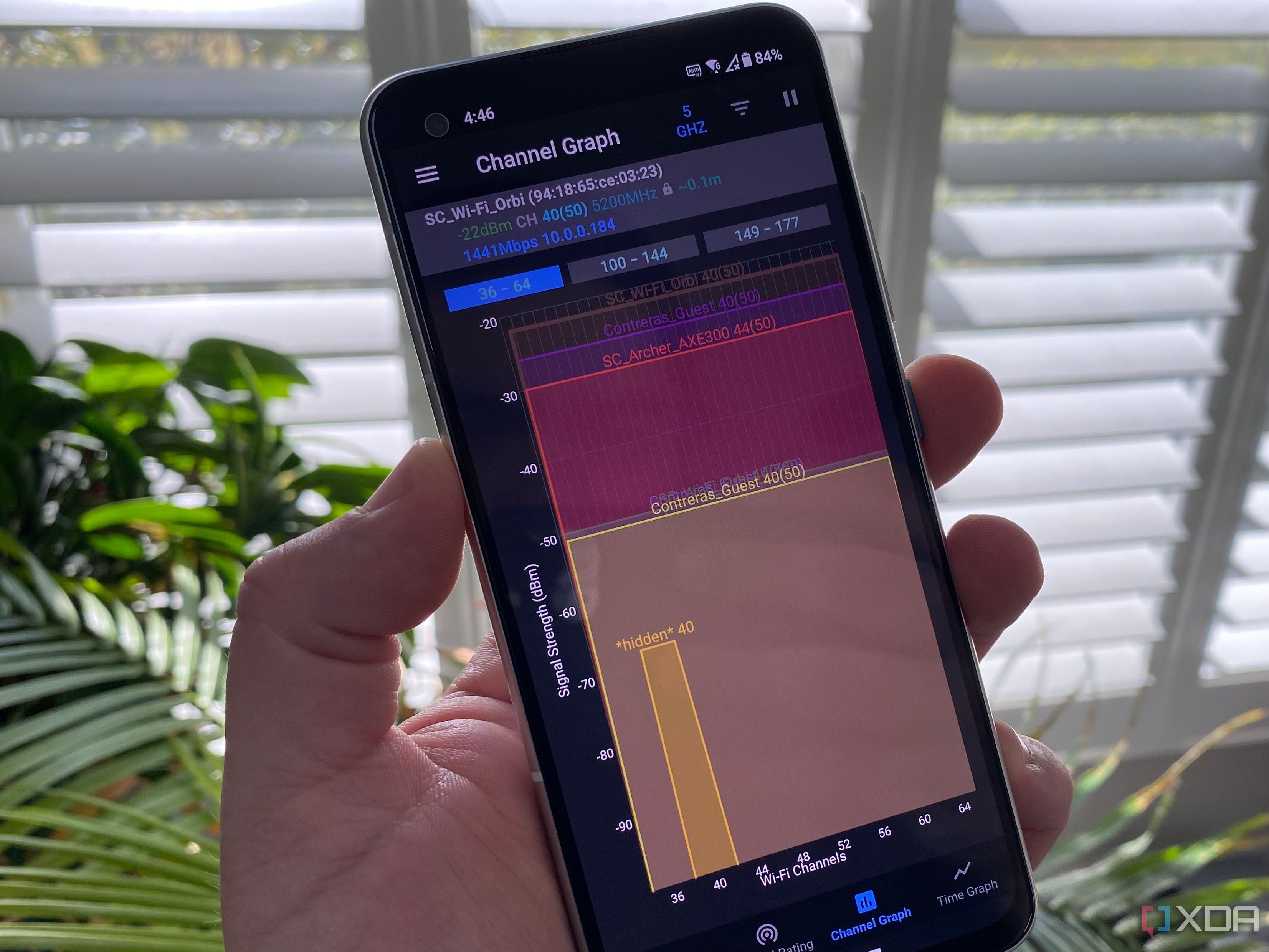
Network congestion is a major issue, especially for those living in apartments, townhouses, or other areas with many homes close together. While routers made for Wi-Fi 7 or Wi-Fi 6/6E have ways around the congestion, namely another radio that broadcasts in the 6GHz range, those with older routers still have some options available to reduce the issue. The source of the problem is also, oddly enough, the way to fix it, as most routers never get changed from the defaults. That means changing the default channel for a less congested one makes your Wi-Fi better, but it also helps the wireless signal of all your neighbors too, as you’re not interfering with their signals anymore.
Open up your router’s management pages and find the Wi-Fi settings page. You’ll want to change the channel used on both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands (if your router has 6GHz as well, you can leave that as it’s less likely to be congested). Depending on what your neighbors have their settings at, you might need to use lower or higher channel numbers than the default. Some routers also scan to see which channels are less congested, and they’ll either tell you on the settings page or automatically change the channel for you. If you want to be sure you’re not using a congested channel, there are apps you can install on your phone that will tell you which channels are more crowded, so you know which to switch to.

Related
2.4GHz vs 5GHz: Which band should you use for your home WiFi?
Pick the right band on your router depending on your use case.
5 Adjust the router antennas
External antennas aren’t just for show
If your wireless router has external antennas, one way to improve your Wi-Fi signal is to angle them for better coverage. How you angle them will depend on a few things, mainly on how many antennas you have, but also on where you want the signal to go. For the majority of routers with external antennas, the omni-directional antenna means the signal is spread in a donut shape, with the antenna in the center, as if it were an axle on a wheel. That means if they’re all pointing at the ceiling, most of the signal will be spread horizontally, not vertically. To make the signal also go vertical, have at least one antenna parallel to the floor but at right angles to the router and one pointing directly back from the device.
Users of routers with internal antennas don’t have to worry about the orientation of the router, as they’re designed to cover a more spherical area. Directional antennas are also a thing, but they’re not often found on consumer-level equipment. These would be things like panel or yagi-style antennas, which are designed to beam Wi-Fi in one specific direction. You could put one outside your home to send Wi-Fi directly to a shed or firepit further down your yard. Also remember that turning the gain up will benefit users further away from the router, while it could degrade the experience of users in the same room.

Related
Why the antennas on your router matter, and the direction you should point them in
Those antennas on your router might make it look like a spider, but here’s why they make your web better
4 Limit unnecessary connections
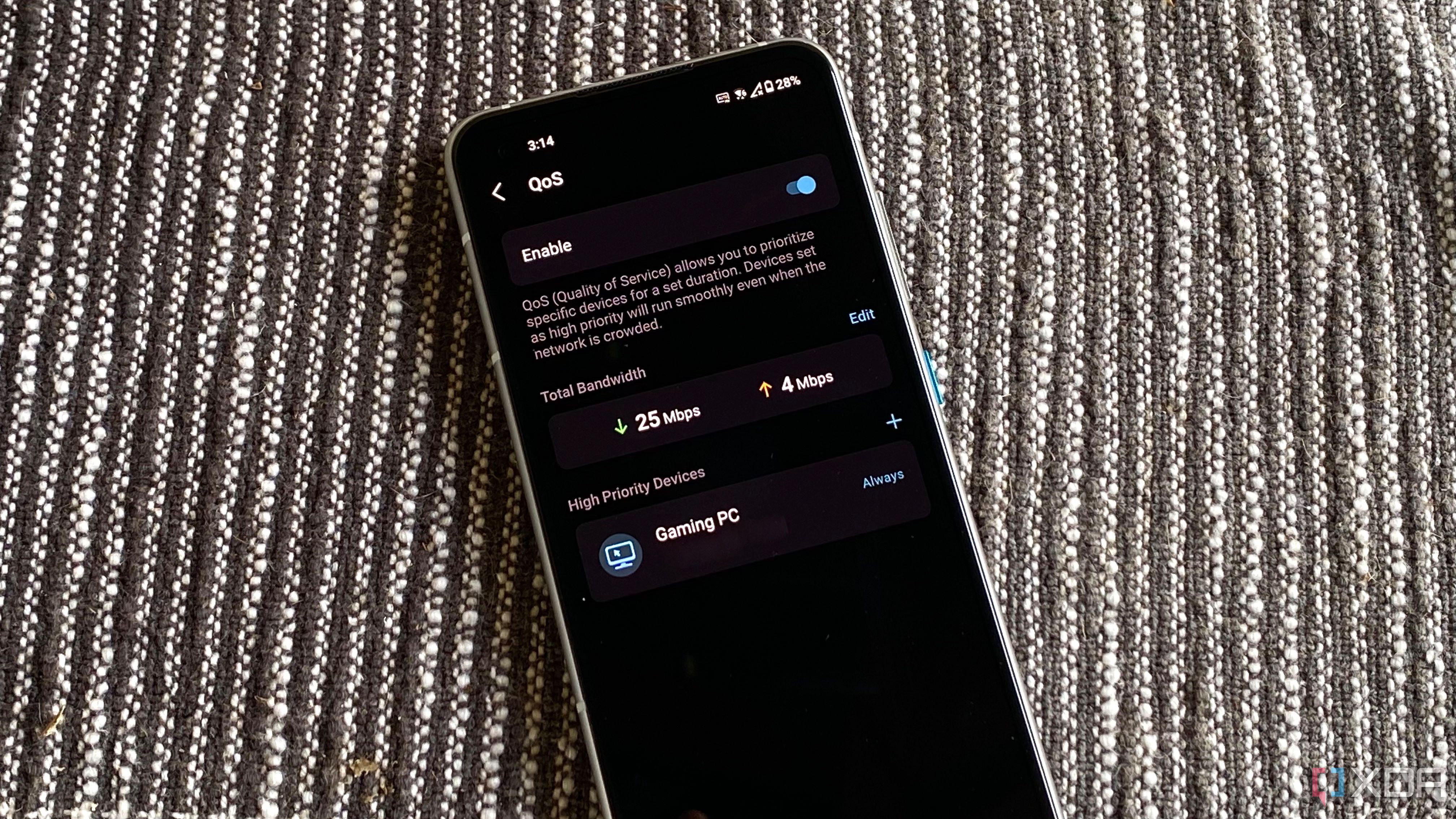
Setting up Quality-of-Service (QoS) is invaluable
If you have many devices and users on your network, one of the most important router settings is Quality of Service, or QoS. This feature works like the Express or HOV lanes on the freeway, sorting network traffic so that your most important devices and services get more bandwidth. Services that don’t need priority queuing get deprioritized, like running updates or backups to a NAS. That means your games and video conferences get the bandwidth they need for a speedy connection, keeping your feed clear and your latency low. The best part is that the services put on slower tiers might not even notice it, as QoS ranks the priority based on options you choose, plus known properties of programs that are less affected by latency issues.
Related
5 reasons why you should set up QoS prioritization on your router for better internet
How to get better internet with no new hardware
3 Reboot your router and modem
Cache issues can slow your Wi-Fi, but there’s a simple fix
One of the first troubleshooting steps for many computing devices is to turn it off and back on again. Surprisingly, this also holds true for Wi-Fi routers in some conditions, but not for the reasons you might think. Newer routers have plenty of memory and storage for cache and other working data, so while a reboot does clear cache, it is unlikely to fix things if you have Wi-Fi issues. But newer routers test for interference when booting up, so you might fix the issue by hopping to a clearer channel for broadcasting.

Related
How to fix: Router doesn’t connect to the internet after a reset
If you reset your router and can’t connect to the internet after, there are some quick steps to help get you back online.
2 Scan for malware
Computer viruses can slow down your internet
Hackers have gotten more sophisticated, and your home network is always going to be a target. You don’t have to be running Windows XP to get malware or other nasties from the internet, simply having a router that’s not updated to the latest security patches could potentially mark you as worthy of attack. Most attacks are fairly automated these days, so they don’t even have to do anything to get malware onto your system. Once it’s installed, it will siphon off your data, and send it out of your home network to a control server.
That process of scanning and egress of data will slow down your network, and your Wi-Fi will suffer because of it. Running Malwarebytes or any other modern antivirus and antimalware service will hopefully find the cause of the slowdown and help you remove it. Just, make sure you’re downloading the antivirus program from a trusted source, like the original company’s website, because fake antivirus installers are a real problem.
Related
Best antivirus for Windows 11
Protecting your data is always important, and when the built-in Windows security fails, these antivirus programs are your best bet.
1 Move your router
Wi-Fi works best when not blocked
While other wireless connections can interfere with your Wi-Fi, physical objects can also. It’s all too tempting to put your router on a shelf behind things or behind the TV so you can’t see it. However, that’s not a good idea for the best Wi-Fi signal you can get, as walls and objects interfere with the signal. Also, avoid putting it near electrical panels or the microwave, as these create their own electrical signals that can cause issues. As we now know how the antennas send out the signal, it also makes more sense to have the router central to your home. Even moving it to the other side of the room where the internet jack is can make a big difference in signal speeds, and it’s relatively easy to do.
Slow Wi-Fi sucks, but you can make it faster without new hardware
Most of us need Wi-Fi as part of daily life, and speed issues are never fun. However, you can boost the performance of your wireless connection with a few clicks, assuming that congestion is the reason for the slow speeds. It could also be that your router is just old, and using a Wi-Fi version that was fast at the time, but has been eclipsed by newer standards. The only thing that will fix speeds in that case is an upgrade, but it’s worth trying the free options first.

Related
You can boost your router’s signal with tinfoil, here’s how
A little-known trick to boost your router’s signal is a sheet of tinfoil, but it won’t always work.